FOOD SAFETY TRAINING AND CERTIFICATION
WHAT IS FOSTAC?
FOSTAC (Food Safety Training & Certification) is a crucial initiative by Food Safety and
Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) in 2018, Its goal is to ensure that individuals
involved in food handling, preparation, and service are knowledgeable about and adhere to
essential food safety standards. By offering structured training and certification, FOSTAC
helps food businesses meet regulatory requirements, enhance food safety practices, and boost
operational efficiency. Adherence to FOSTAC training and certification contributes to a safer
food supply chain Across INDIA and builds consumer trust in food products.
HOW DO WE PLAN FOSTAC TRAINING FOR FOOD BUSINESS OPERATORS & FOOD HANDLERS?
Planning FOSTAC (Food Safety Training and Certification) training involves several key
steps to ensure that the training program is effective, comprehensive, and tailored to the
specific needs of food business operators & food handlers. Here's a general outline of
how to plan FOSTAC training.
1. Identify Training Needs: Assess the training needs of food business operators & food handlers by considering factors such as the type of food business, the size of the operation, the level of existing knowledge and skills among staff, and any specific regulatory requirements or industry standards applicable to the business.
2. Select Training Provider: Choose a .... reputable training provider or organization accredited to deliver FOSTAC training. Verify that the provider meets all necessary qualifications and has experience delivering effective food safety training programs.
3. Customize Training Content: Work with the training provider to customize the training content to address the specific needs and requirements of the food business operators & food handlers. Ensure that the training covers essential topics such as personal hygiene, food handling practices, sanitation procedures, allergen management, and regulatory compliance.
4. Determine Training Methodology: Determine the most appropriate training methodology based on factors such as the size of the target audience, available resources, and learning preferences. Options may include in-person workshops, online courses, self paced modules, or a combination of formats.
5. Schedule Training Sessions: Coordinate with the training provider to schedule training sessions at convenient times for food business operators & food handlers. Consider factors such as work schedules, peak business hours, and staff availability to maximize participation and minimize disruptions to business operations.
6. Communicate Training Details: Inform food business operators & food handlers about the upcoming training sessions, including the date, time, location, and any preparation or prerequisites required. Provide clear instructions on how to register or sign up for the training and address any questions or concerns they may have.
7. Deliver Training: Conduct the training sessions according to the planned schedule and methodology. Ensure that training materials are engaging, interactive, and relevant to the needs of the participants. Encourage active participation, questions, and discussions to enhance learning outcomes.
8. Assess Learning Outcomes: Evaluate the effectiveness of the training program by assessing participants' knowledge and skills before and after the training. Use quizzes, tests, or practical demonstrations to measure learning outcomes and identify areas for improvement.
9. Provide Certification: Issue FOSTAC certificates or other documentation to participants who successfully complete the training program. Certificates should clearly indicate the name of the participant, the training program completed, and the date of completion.
10. Follow-Up and Continuous Improvement: Follow up with participants after the training to gather feedback on their experience and identify opportunities for improvement. Use this feedback to refine future training programs and ensure ongoing compliance with food safety standards.
1. Identify Training Needs: Assess the training needs of food business operators & food handlers by considering factors such as the type of food business, the size of the operation, the level of existing knowledge and skills among staff, and any specific regulatory requirements or industry standards applicable to the business.
2. Select Training Provider: Choose a .... reputable training provider or organization accredited to deliver FOSTAC training. Verify that the provider meets all necessary qualifications and has experience delivering effective food safety training programs.
3. Customize Training Content: Work with the training provider to customize the training content to address the specific needs and requirements of the food business operators & food handlers. Ensure that the training covers essential topics such as personal hygiene, food handling practices, sanitation procedures, allergen management, and regulatory compliance.
4. Determine Training Methodology: Determine the most appropriate training methodology based on factors such as the size of the target audience, available resources, and learning preferences. Options may include in-person workshops, online courses, self paced modules, or a combination of formats.
5. Schedule Training Sessions: Coordinate with the training provider to schedule training sessions at convenient times for food business operators & food handlers. Consider factors such as work schedules, peak business hours, and staff availability to maximize participation and minimize disruptions to business operations.
6. Communicate Training Details: Inform food business operators & food handlers about the upcoming training sessions, including the date, time, location, and any preparation or prerequisites required. Provide clear instructions on how to register or sign up for the training and address any questions or concerns they may have.
7. Deliver Training: Conduct the training sessions according to the planned schedule and methodology. Ensure that training materials are engaging, interactive, and relevant to the needs of the participants. Encourage active participation, questions, and discussions to enhance learning outcomes.
8. Assess Learning Outcomes: Evaluate the effectiveness of the training program by assessing participants' knowledge and skills before and after the training. Use quizzes, tests, or practical demonstrations to measure learning outcomes and identify areas for improvement.
9. Provide Certification: Issue FOSTAC certificates or other documentation to participants who successfully complete the training program. Certificates should clearly indicate the name of the participant, the training program completed, and the date of completion.
10. Follow-Up and Continuous Improvement: Follow up with participants after the training to gather feedback on their experience and identify opportunities for improvement. Use this feedback to refine future training programs and ensure ongoing compliance with food safety standards.
BENEFITS AND NECESSARY OF FOSTAC
1. Enhanced Food Safety Knowledge: FOSTAC provides comprehensive training on best
practices for food handling, preparation, and storage. This helps reduce the risk of foodborne
illnesses and contamination.
2. Regulatory Compliance: Certification ensures that food businesses comply with local and international food safety regulations. This helps avoid legal issues ....and potential fines associated with non-compliance.
3. Improved Quality of Food: By following FOSTAC guidelines, food establishments can maintain high standards of hygiene and quality, leading to better-tasting and safer food.
4. Increased Consumer Confidence: Certification demonstrates to customers that a food business prioritizes safety and hygiene, which can enhance trust and attract more customers.
5. Reduced Risk of Foodborne Illnesses: Proper training and adherence to safety standards significantly decrease the likelihood of foodborne illnesses, protecting both consumers and employees.
6. Better Management of Food Allergens: FOSTAC training includes managing food allergens effectively, helping to prevent allergic reactions and ensuring that food is safe for all consumers.
7. Enhanced Employee Training: It provides a structured approach to training employees, ensuring that everyone is on the same page regarding food safety practices.
8. Cost Savings: By preventing food contamination and reducing waste through proper handling and storage practices, businesses can save money in the long run.
9. Competitive Advantage: Certification can differentiate a business from competitors by showcasing a commitment to high standards of food safety.
10. Support for Business Growth: As food safety regulations become more stringent, having FOSTAC certification can facilitate smoother expansion into new markets or regions.
2. Regulatory Compliance: Certification ensures that food businesses comply with local and international food safety regulations. This helps avoid legal issues ....and potential fines associated with non-compliance.
3. Improved Quality of Food: By following FOSTAC guidelines, food establishments can maintain high standards of hygiene and quality, leading to better-tasting and safer food.
4. Increased Consumer Confidence: Certification demonstrates to customers that a food business prioritizes safety and hygiene, which can enhance trust and attract more customers.
5. Reduced Risk of Foodborne Illnesses: Proper training and adherence to safety standards significantly decrease the likelihood of foodborne illnesses, protecting both consumers and employees.
6. Better Management of Food Allergens: FOSTAC training includes managing food allergens effectively, helping to prevent allergic reactions and ensuring that food is safe for all consumers.
7. Enhanced Employee Training: It provides a structured approach to training employees, ensuring that everyone is on the same page regarding food safety practices.
8. Cost Savings: By preventing food contamination and reducing waste through proper handling and storage practices, businesses can save money in the long run.
9. Competitive Advantage: Certification can differentiate a business from competitors by showcasing a commitment to high standards of food safety.
10. Support for Business Growth: As food safety regulations become more stringent, having FOSTAC certification can facilitate smoother expansion into new markets or regions.
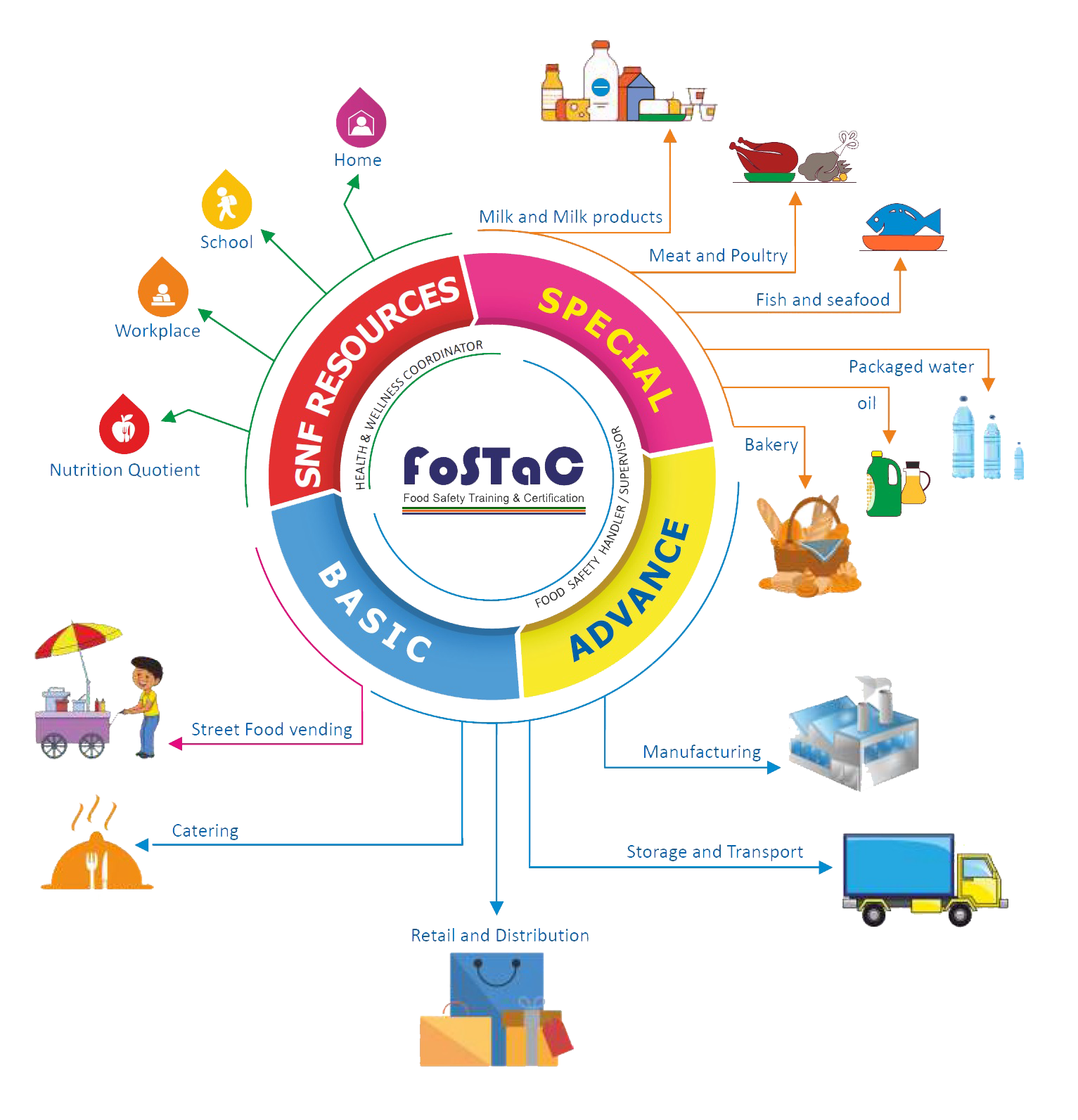
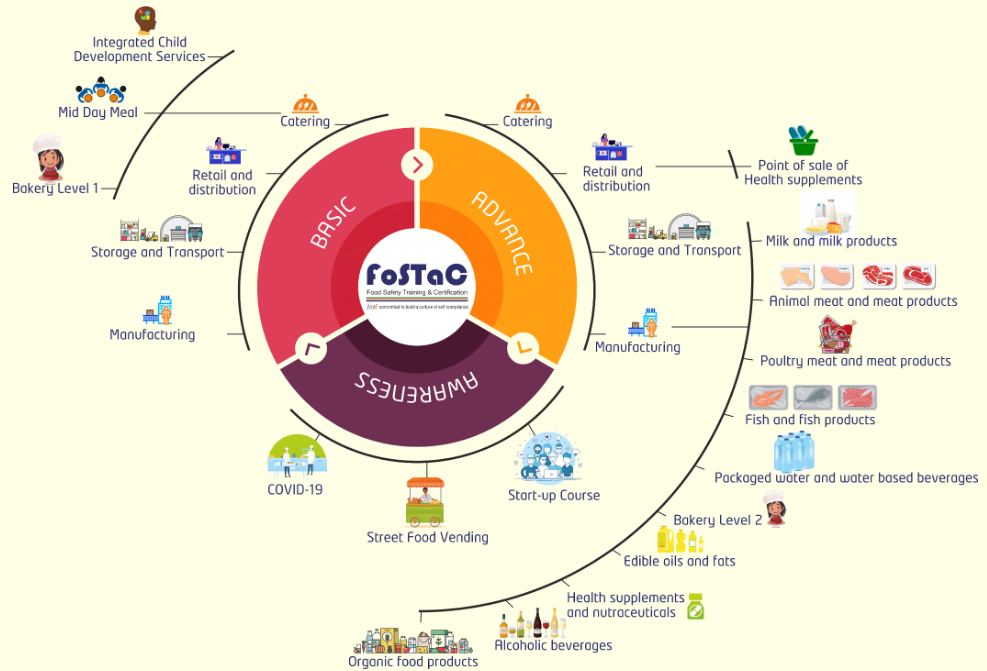
TYPES OF FOSTAC TRAININGS:
1. Retail and Distribution (Basic and Advanced)
2. Catering (Basic and Advanced)
3. Advance Manufacturing
4. Manufacturing Special: Milk and milk products, Oil and fats, water and water-based beverages.
2. Catering (Basic and Advanced)
3. Advance Manufacturing
4. Manufacturing Special: Milk and milk products, Oil and fats, water and water-based beverages.
CONSEQUENCES OF NOT PARTICIPATING IN FOSTAC
REGULATORY AND LEGAL COMPLIANCE ISSUES FOR NOT PARTICIPATING IN FOSTAC (WHAT HAPPENS IF NO FOSTAC)
1. Violation of Food Safety Regulations:
o Legal Penalties: Many jurisdictions mandate food safety certifications to operate legally. Not having FOSTAC certification may result in violations of local and national food safety laws, leading to fines, sanctions, or legal actions.
o License Revocation: In some cases, businesses might face suspension or revocation of their operating licenses if they fail to meet required food safety standards.
2. Non-Compliance with Industry Standards:
o Regulatory Inspections: Food safety authorities conduct inspections to ensure compliance with established standards..... Lack of certification can lead to failed inspections, enforcement actions, and mandates for corrective measures.
o Sanctions and Restrictions: Businesses may face restrictions on their operations or additional regulatory scrutiny if they do not meet required food safety standards.
3. Increased Risk of Legal Action:
o Liability for Foodborne Illnesses: If a foodborne illness outbreak is traced back to a lack of adherence to food safety protocols, the business could face significant legal liability, including lawsuits and compensation claims.
o Legal Costs: Legal actions resulting from food safety issues can lead to substantial legal fees and financial liabilities for the business.
4. Insurance and Financial Risks:
o Insurance Claims Denials: Without proper certification, businesses may find it difficult to secure insurance coverage or may face denials of claims related to food safety incidents.
o Higher Insurance Premiums: Insurance providers may view uncertified businesses as higher risks, resulting in increased premiums or reduced coverage options.
5. Operational and Financial Consequences:
o Operational Restrictions: Regulatory authorities may impose operational restrictions or require significant changes to business practices if certification requirements are not met.
o Costly Reworks: Businesses may incur additional costs to address non-compliance issues, such as implementing corrective actions, retraining staff, or upgrading facilities.
6. Market Access Limitations:
o Loss of Business Opportunities: Some markets and clients require food safety certification as a precondition for partnerships or contracts. Lack of certification can limit access to these opportunities.
o Competitive Disadvantage: Businesses without certification may be at a competitive disadvantage compared to those that meet or exceed regulatory requirements.
7. Damage to Business Reputation:
o Public Relations Issues: Non-compliance can harm the business’s reputation, leading to negative publicity and loss of customer trust.
o Consumer Confidence: Customers may be less likely to patronize a business that does not demonstrate adherence to food safety standards, impacting revenue and growth.
o Legal Penalties: Many jurisdictions mandate food safety certifications to operate legally. Not having FOSTAC certification may result in violations of local and national food safety laws, leading to fines, sanctions, or legal actions.
o License Revocation: In some cases, businesses might face suspension or revocation of their operating licenses if they fail to meet required food safety standards.
2. Non-Compliance with Industry Standards:
o Regulatory Inspections: Food safety authorities conduct inspections to ensure compliance with established standards..... Lack of certification can lead to failed inspections, enforcement actions, and mandates for corrective measures.
o Sanctions and Restrictions: Businesses may face restrictions on their operations or additional regulatory scrutiny if they do not meet required food safety standards.
3. Increased Risk of Legal Action:
o Liability for Foodborne Illnesses: If a foodborne illness outbreak is traced back to a lack of adherence to food safety protocols, the business could face significant legal liability, including lawsuits and compensation claims.
o Legal Costs: Legal actions resulting from food safety issues can lead to substantial legal fees and financial liabilities for the business.
4. Insurance and Financial Risks:
o Insurance Claims Denials: Without proper certification, businesses may find it difficult to secure insurance coverage or may face denials of claims related to food safety incidents.
o Higher Insurance Premiums: Insurance providers may view uncertified businesses as higher risks, resulting in increased premiums or reduced coverage options.
5. Operational and Financial Consequences:
o Operational Restrictions: Regulatory authorities may impose operational restrictions or require significant changes to business practices if certification requirements are not met.
o Costly Reworks: Businesses may incur additional costs to address non-compliance issues, such as implementing corrective actions, retraining staff, or upgrading facilities.
6. Market Access Limitations:
o Loss of Business Opportunities: Some markets and clients require food safety certification as a precondition for partnerships or contracts. Lack of certification can limit access to these opportunities.
o Competitive Disadvantage: Businesses without certification may be at a competitive disadvantage compared to those that meet or exceed regulatory requirements.
7. Damage to Business Reputation:
o Public Relations Issues: Non-compliance can harm the business’s reputation, leading to negative publicity and loss of customer trust.
o Consumer Confidence: Customers may be less likely to patronize a business that does not demonstrate adherence to food safety standards, impacting revenue and growth.
FOSTAC FOR WHOM & WHO SHOULD ENROLL FOR FOSTAC?
HOTELS, CATERERS, RETAIL & DISTRIBUTION, STREET FOOD VENDORS, CONDIMENTS, BAKERIES, MANUFACTURERS, MILK & MILK PRODUCTS, OIL & FATS, PROVISION STORES, WATER & BEVERAGES, MEAT & POULTRY
FOSTAC (Food Safety Training and Certification) is a certification program designed
primarily for individuals and organizations involved in the food industry. Here’s a
breakdown of who benefits from FOSTAC training:
1. Food Safety Supervisors: Individuals responsible for overseeing food safety practices within establishments, such as restaurants, food processing units, or catering services. They ensure that the staff follows proper food handling, storage, and sanitation procedures.
2. Food Handlers(employees): This includes anyone directly involved in the preparation, handling, or serving of food. Proper training helps them understand and implement safe food practices to prevent contamination and ensure food safety.
3. Managers and Owners: Food business operators and managers who need to ensure their establishment complies with food safety regulations and standards. FOSTAC training can help them understand the requirements and oversee compliance.
4. Quality Assurance Personnel: Those involved in monitoring and ensuring that food products meet safety standards. They can use the training to better manage quality control processes.
5. Regulatory Authorities: In some cases, individuals involved in enforcing food safety regulations might also benefit from understanding the FOSTAC framework and its standards.
1. Food Safety Supervisors: Individuals responsible for overseeing food safety practices within establishments, such as restaurants, food processing units, or catering services. They ensure that the staff follows proper food handling, storage, and sanitation procedures.
2. Food Handlers(employees): This includes anyone directly involved in the preparation, handling, or serving of food. Proper training helps them understand and implement safe food practices to prevent contamination and ensure food safety.
3. Managers and Owners: Food business operators and managers who need to ensure their establishment complies with food safety regulations and standards. FOSTAC training can help them understand the requirements and oversee compliance.
4. Quality Assurance Personnel: Those involved in monitoring and ensuring that food products meet safety standards. They can use the training to better manage quality control processes.
5. Regulatory Authorities: In some cases, individuals involved in enforcing food safety regulations might also benefit from understanding the FOSTAC framework and its standards.

